
laparoscopy and laser Centre

laparoscopy and laser Centre
Laparoscopy, also known as minimal invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. During the surgery, the surgeon uses the thin long instrument, laparoscope which is connected to a high definition camera and monitor ,to visualize the organs, tissues, and structures inside the abdomen. The procedure can involve a wide range of operations, including
small incisions result in smaller scars, leading to better cosmetic outcomes and reduced post-operative discomfort.
Due to the smaller incisions, there is a lower risk of complications such as infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding tissues.
Better visualization and precision during the procedure.
Laparoscopic surgery typically involves less blood loss.
LAPSER is the best laparoscopic hospital in Chennai dealing with basic and advanced laparoscopic treatments for Gastroenetrology, Urology and Gynaecological diseases. It is best to consult with our qualified surgeon who can evaluate your specific condition and recommend the most appropriate surgery options.
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimal invasive surgery, involves using small incisions and specialized instruments to perform surgical procedures.
A laparoscope, a thin tube with a high definition camera which is connected to monitor, is inserted through a small incision, allowing surgeons to view the internal organs and operate.
Benefits include shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery, reduced pain, and smaller scars.
Cholelithiasis or gall stone disease refers to the presence of stones cholesterol or pigmented in gallbladder and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of migrated gallstones within bile ducts.The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that's released into your small intestine.Gallstones may vary in sizeand number.
Risk factors for gallstones include birth control pills, pregnancy, a family history of gallstones, obesity, diabetes, liver disease, or rapid weight loss.
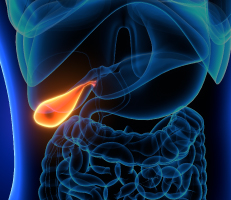
Gallstones are mostly asymptomatic. Treatment for gallstones is indicated based on thesymptoms and the results of diagnostic testing. Your doctor may recommend that you be alert for signs &symptoms of gallstone and its complications. If occur in the future, you can have treatment.
Surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). It is recommended to surgically removing your gallbladder, since gallstones frequently recur. Once your gallbladder is removed, bile flows directly from your liver into your small intestine, rather than being stored in your gallbladder.
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or other body part protrudes through the wall of muscle or tissue that normally contains it. Most hernias occur within the abdominal cavity, between the chest and the hips. Types of herina are Umbilical hernia, Para umbilical hernia, Inguinal Hernia and Incisional hernia.
Inguinal hernia's occur when a part or whole of the abdominal contents omentum or intestine protrudes through a weak spot in the anterior abdominal wall – inguinal canal
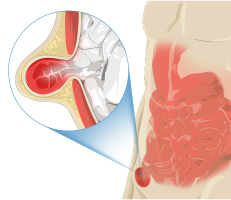
An umbilical hernia is a bulge in bellybutton (navel) which occurs due to a defect in umbilicus through which intestine or omentumprotrudes. Umbilical hernias are common and typically harmless.
Umbilical hernias are most common in infants, but they can affect adults as well. In an infant, an umbilical hernia may be especially evident when the infant cries, causing the bellybutton to protrude. This is a classic sign of an umbilical hernia
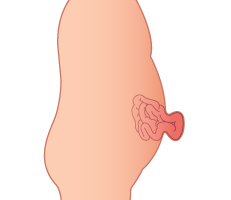
An umbilical hernia is a soft swelling or bulge in the navel. In babies with umbilical hernia, the bulge may be visible only cry, cough or strain.
Umbilical hernias that appear during adulthood may have symptoms .
An umbilical hernia is diagnosed during a physical exam. Imaging studies — such as an abdominal ultrasound or a CT scan — are used to screen for complications.
Most umbilical hernias in babies close on their own by age 1 or 2. For child, surgery is typically reserved for umbilical hernias that:
For adults, surgery is typically recommended to avoid possible complications, especially if the umbilical hernia gets bigger or becomes painful.
This procedure is done with local anaesthesia /spinal anaesthesia or general anaesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision below umbilicus and pushes the protruding contents back into abdomen. Then the weakened area is often reinforced with a synthetic mesh .The opening is then closed with stitches, staples or surgical glue.
This procedure requiring general anaesthesia, the surgeon makes small incisions to get in to your abdomen. Gas is used to inflate your abdomen to make the internal organs easier to see. After reducing the herniated contents mesh is placed &anchored to anterior abdominal wall. Advantages are less discomfort and scarring after surgery and a quicker return to normal activities.
Appendicitis is an infection& inflammation of the appendix, a tubular structure that projects from the colon on the right lower side of abdomen.
Appendicitis causes pain in your lower right abdomen. However, in most patients, pain begins around the umbilicus and then migrates. As inflammation worsens, appendicitis pain typically increases and eventually becomes severe.
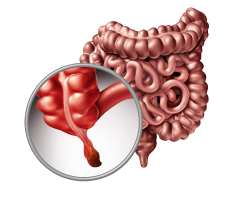
Diagnosis of appendicitis is mostly made out clinically but sometimes requires a imaging to confirm the disease and its complications. Tests and procedures used to diagnose appendicitis include:
Appendicitis treatment usually involves surgery to remove the inflamed appendix. Before surgery you may be given a dose of antibiotics to treat infection.
In general, laparoscopic surgery allows you to recover faster and heal with less pain and scarring. It may be better for older adults and people with obesity.
But laparoscopic surgery isn't appropriate for everyone. If your appendix has ruptured and infection has spread beyond the appendix or you have an abscess, you may need an open appendectomy, which allows your surgeon to clean the abdominal cavity.
If appendix has burst and an abscess has formed around it, the abscess may be drained by placing a tube through your skin into the abscess. Interval Appendectomy can be performed several weeks later after controlling the infection.
Make an appointment with a doctor if you have signs or symptoms. Severe abdominal pain requires immediate attention.