
laparoscopy and laser Centre

laparoscopy and laser Centre
General surgery is a surgical specialty that focuses on the sebaceous cyst, dermoid cyst, mole removal and diabetic foot ulcer.
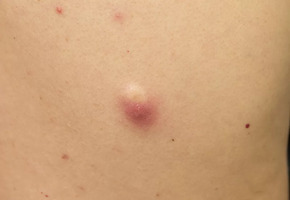
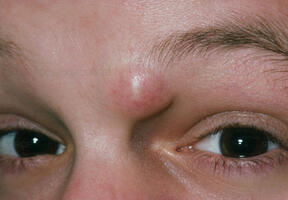
cysts are soft, white or yellow lumps that slowly grow under the skin due to a clogged hair follicle or trauma, like a scratch. They are filled with a thick, oily substance that may drain out. Painless and otherwise harmless, sebaceous cysts can sometimes get infected.
Sebaceous cysts can be easily moved under the skin. While they can pop up anywhere on the body, they are commonly found on the head, back of the ears, neck, and trunk

If sebaceous cyst grows and becomes symptomatic then surgical removal of the cyst is required using local anasthesia.
A dermoid cyst is a saclike growth that is present at birth. It contains structures such as hair, fluid, teeth, or skin glands that can be found on or in the skin.
Dermoid cysts grow slowly and are not tender unless ruptured. They usually occur on the face, inside the skull, on the lower back, and in the ovaries. Superficial dermoid cysts on the face usually can be removed without complications. Removal of other, more raredermoid cysts requires special techniques and training.

Dermoid cysts in the brain: Dermoid cysts occur very rarely here. A neurosurgeon may need to remove them if they cause problems.
Dermoid cysts in the nasal sinuses: : These are also very rare. Only a handful of cases involving dermoid cysts located here are reported each year. Removal of these cysts is extremely complicated.
Ovarian dermoid cysts: These growths can develop in a woman during their reproductive years. They can cause torsion, infection, rupture, and cancer. These dermoid cysts can be removed with either conventional surgery or laparoscopy (surgery that uses small incisions and specially designed instruments to enter the abdomen or pelvis).
Dermoid cysts of the spinal cord: A sinus tract, which is a narrow connection from a deep pit in the skin, usually connects these very rare cysts to the skin surface. This type of dermoid cyst can become infected. Removal is often incomplete, but the outcome is usually excellent.
Many people with dermoid cysts have no symptoms. Some people start to experience symptoms as their cysts grow. Symptoms vary based on the type of dermoid cyst. For example:
Periorbital dermoid cyst: A lump near the edge of your eyebrow may be swollen and have a yellow tint. Over time, it can change the shape of bones in the area.
Ovarian dermoid cyst: You may have pain in your pelvic area, particularly around the time of menstruation.
Spinal dermoid cyst: A growing dermoid cyst may compress your spinal cord or nerves, causing:
Surgical removal is the only effective treatment for any type of dermoid cyst.
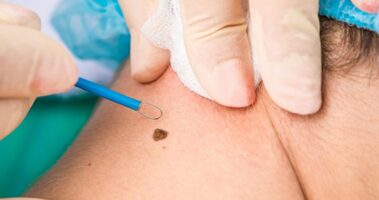
Moles (nevi) are a common type of skin growth. They often appear as small, dark brown spots and are caused by clusters of pigment-forming cells (melanocytes). Most people have 10 to 40 moles that appear during childhood and adolescence and may change in appearance or fade over time.
Most moles are harmless. Rarely, they become cancerous. Being aware of changes in your moles and other pigmented patches is important to detecting skin cancer, especially malignant melanoma.

Make an appointment with your doctor if a mole looks unusual, grows or otherwise changes.
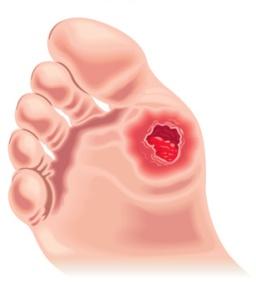
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur if you have diabetes. High blood sugar (glucose) can injure nerves throughout the body. Diabetic neuropathy most often damages nerves in the legs and feet.
Depending on the affected nerves, diabetic neuropathy symptoms include pain and numbness in the legs, feet and hands. It can also cause problems with the digestive system, urinary tract, blood vessels and heart. Some people have mild symptoms. But for others, diabetic neuropathy can be quite painful and disabling.

Your health care provider can usually diagnose diabetic neuropathy by performing a physical exam and carefully reviewing your symptoms and medical history.